Internal Data Structure
1The Cassandra data model is a schema-optional, column-oriented data model. This means that, unlike a relational database, you do not need to model all of the columns required by your application up front, as each row is not required to have the same set of columns.
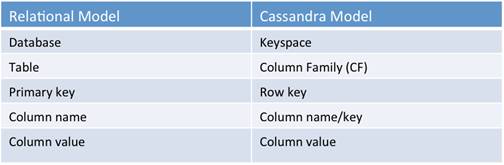
2The Cassandra data model consists of keyspaces (analogous to databases), column families (analogous to tables in the relational model), keys and columns.
For each column family, don’t think of a relational table. Instead, think of a nested sorted map data structure. A nested sorted map is a more accurate analogy than a relational table, and will help you make the right decisions about your Cassandra data model.
Map<RowKey, SortedMap<ColumnKey, ColumnValue>>
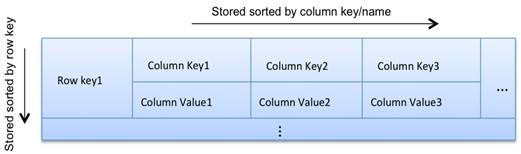
A map gives efficient key lookup, and the sorted nature gives efficient scans. In Cassandra, we can use row keys and column keys to do efficient lookups and range scans. The number of column keys is unbounded. In other words, you can have wide rows.
A key can itself hold a value as part of the key name. In other words, you can have a valueless column.